Dynamic Huffman Coding
Adaptive Huffman coding (also called Dynamic Huffman coding) is an adaptive coding technique based on Huffman coding. It permits building the code as the symbols are being transmitted, having no initial knowledge of source distribution, that allows one-pass encoding and adaptation to changing conditions in data.
Algorithm - Pseudo Code
Update()
q ⇐ leaf(xt)
if (q is the 0-node)
replace q by a parent 0-node with two 0-node children;
q ⇐ left child;
if (q is a sibling of a 0-node)
interchange q with the highest numbered leaf of the same weight.
increment q’s weight by 1;
q ⇐ parent of q
while (q is not root)
interchange q with the highest numbered node of the same weight.
increment q’s weight by 1;
q ⇐ parent of q
increment q’s weight by 1;
Given the following message:
abracadabra
Compression Example
You must compress this message using dynamic huffman coding. You must show the huffman tree at each step, and provide the compressed message.
First we’ll present the details with the probabilities:
| Symbol | Probability | Duplicates | ASCII code in binary |
|---|---|---|---|
| a | 0.454 | 5 | 01100001 |
| b | 0.181 | 2 | 01100010 |
| c | 0.090 | 1 | 01100011 |
| d | 0.090 | 1 | 01100100 |
| r | 0.181 | 2 | 01110010 |
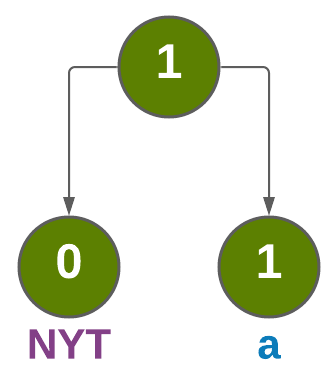
Step 1
Insert ‘a’ and pass 01100001 in ASCII
Step 2
Insert ‘b’ and pass 01100010 in ASCII with its path “0”.
So it’s 001100010

Step 3
Insert ‘r’ and pass 01110010 in ASCII with its path “00”.
So it’s 0001110010

Step 4
Fixing level 1 (left child was bigger than the right so we swapped).

Step 5
Insert ‘a’ with its path “0”, ‘a’ passed before, therefore we don’t need to pass its ASCII code again, we’ll pass only its route to the node which represnt this symbol

Step 6
Insert ‘c’ and pass 01100011 in ASCII with its path “100”.
So it’s 10001100011

Step 7
Fixing level 2 (left child was bigger than the right so we swapped).

Step 8
Insert ‘a’ with its path “0”, ‘a’ passed before, therefore we don’t need to pass its ASCII code again, we’ll pass only its route to the node which represnt this symbol.

Step 9
Insert ‘d’ and pass 01100100 in ASCII with its path “1100”.
So it’s 110001100100

Step 10
Fixing level 3 (left child was bigger than the right so we swapped).

Step 11
Insert ‘a’ with its path “0”, ‘a’ passed before, therefore we don’t need to pass its ASCII code again, we’ll pass only its route to the node which represnt this symbol.

Step 12
Insert ‘b’ with its path “10”, ‘b’ passed before, therefore we don’t need to pass its ASCII code again, we’ll pass only its route to the node which represnt this symbol.

Step 13
Insert ‘r’ with its path “110”, ‘r’ passed before, therefore we don’t need to pass its ASCII code again, we’ll pass only its route to the node which represnt this symbol.

Step 14
Insert ‘a’ with its path “0”, ‘a’ passed before, therefore we don’t need to pass its ASCII code again, we’ll pass only its route to the node which represnt this symbol.

The final message
01100001 001100010 0001110010 0 10001100011 0 110001100100 0 10 110 0




Leave a comment